
The idea
The rapid growth of the Internet of Things fueled the design of devices that are based on microcontrollers, equipped with sensors, and capable of exchanging data. These devices - used, e.g., in smart home applications or to build environmental monitoring stations - enable the collection and analysis of large amounts of data and the development of potentially powerful applications. However, applications are currently limited by the need to exchange collected data via cloud services to use state-of-the-art AI processes, which consumes significant resources in the form of energy, material, and bandwidth. The aim of the TinyAIoT project is to reduce these resource requirements by developing efficient and tiny AI models that can be used on the microcontrollers themselves. This not only extends the range of possible use cases to more powerful applications, but also reduces the required bandwidth of applications, enabling microcontrollers to operate autonomously for several weeks to years.
Network partners
The project will be carried out as a joint project between the University of Münster and Reedu GmbH & Co. KG (Dr. Thomas Bartoschek).

re:edu is a start-up and spin-off from the Institute of Geoinformatics. Since 2018, re:edu is the producer of the senseBox and offers a wide range of services around the senseBox and the fields of Digital Education, Citizen Science and Smart Cities.

The University of Münster participates with the Institute for Geoinformatics(Prof. Dr. Angela Schwering) and the Institute for Business Informatics(Prof. Dr. Fabian Gieseke).
Associated partners
In addition, various application scenarios are to be realized together with four associated partners, Stadtwerke Emsdetten GmbH, Stabsstelle Smart City of the City of Münster, Naturschutzzentrum Kreis Coesfeld e.V. and Hof Homann eG. Additionally, subcontracts are to be awarded to two further companies (opensenselabgGmbH and Budelmann Elektronik GmbH).

Stadtwerke Emsdetten GmbH
Stabstelle Smart City der Stadt Münster

Naturschutzzentrum Kreis Coesfeld e.V.

Hof Homann eG

opensenselabgGmbH

HANZA Tech Solutions GmbH
Resource efficiency
Potential for resource efficiency.
- Microcontroller: Arduino Pro Mini (5 volts) with a power consumption of 22mA under full load and approx. 3.6mA in sleep mode
- Number of IoT devices: 10 billion microcontrollers are assumed for the estimate; estimates are for about 75 billion IoT devices in 2025
Use cases
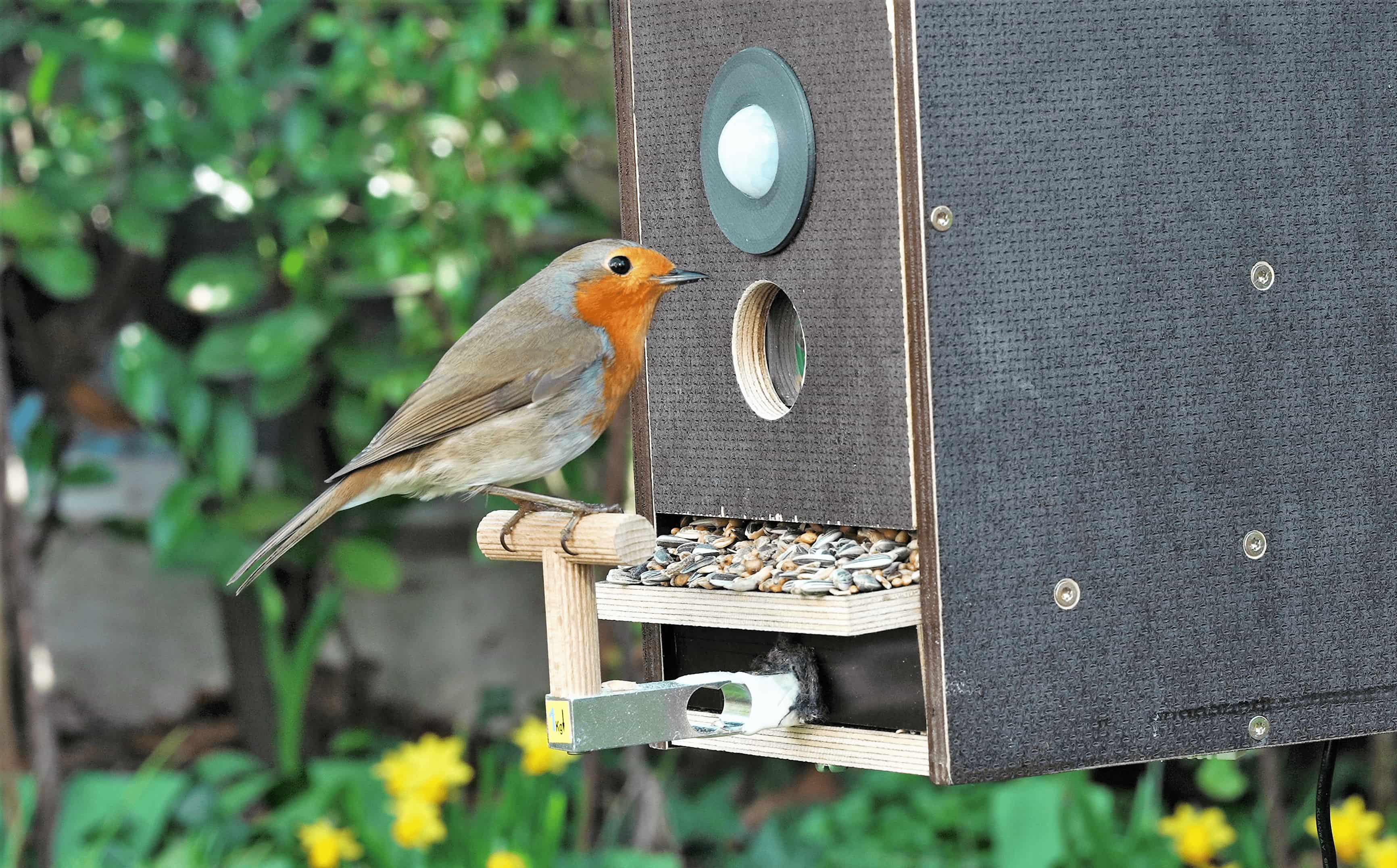

The TinyAIoT project was partly inspired by the existing Birdiary project.
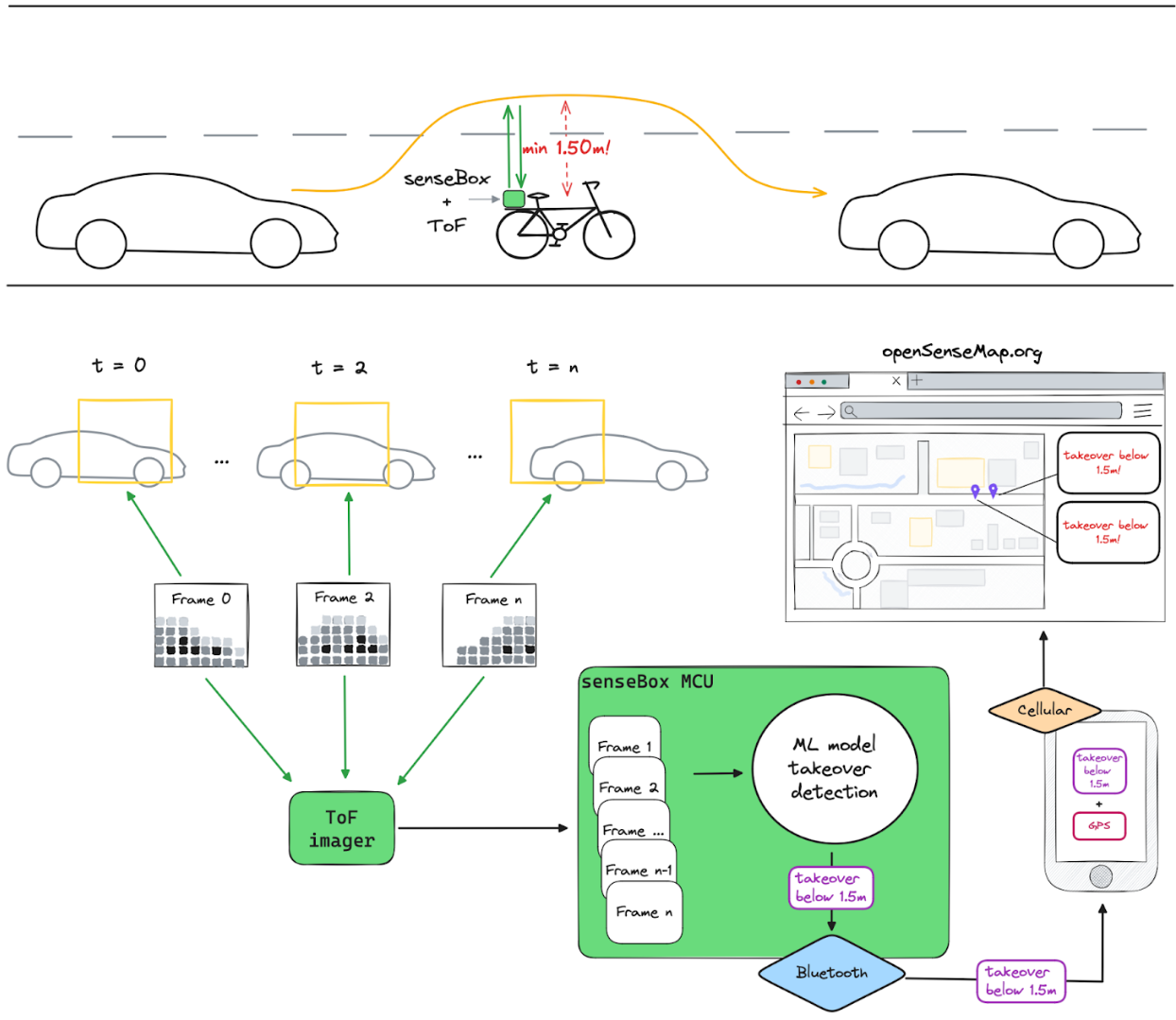
Detecting dangerously close takeover manoeuvres with ToF imaging technology
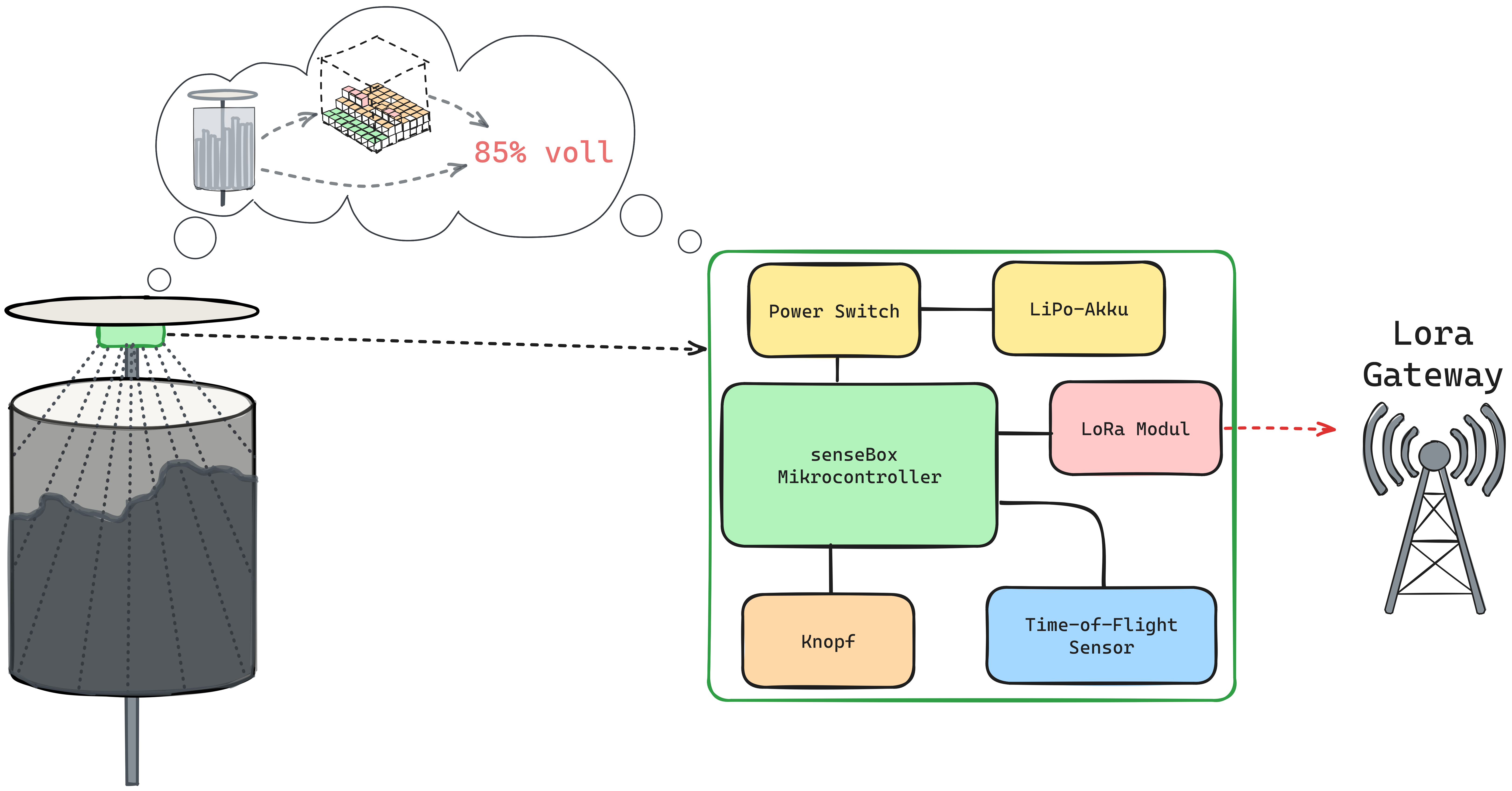
Measuring and sending fill height of public trashcans
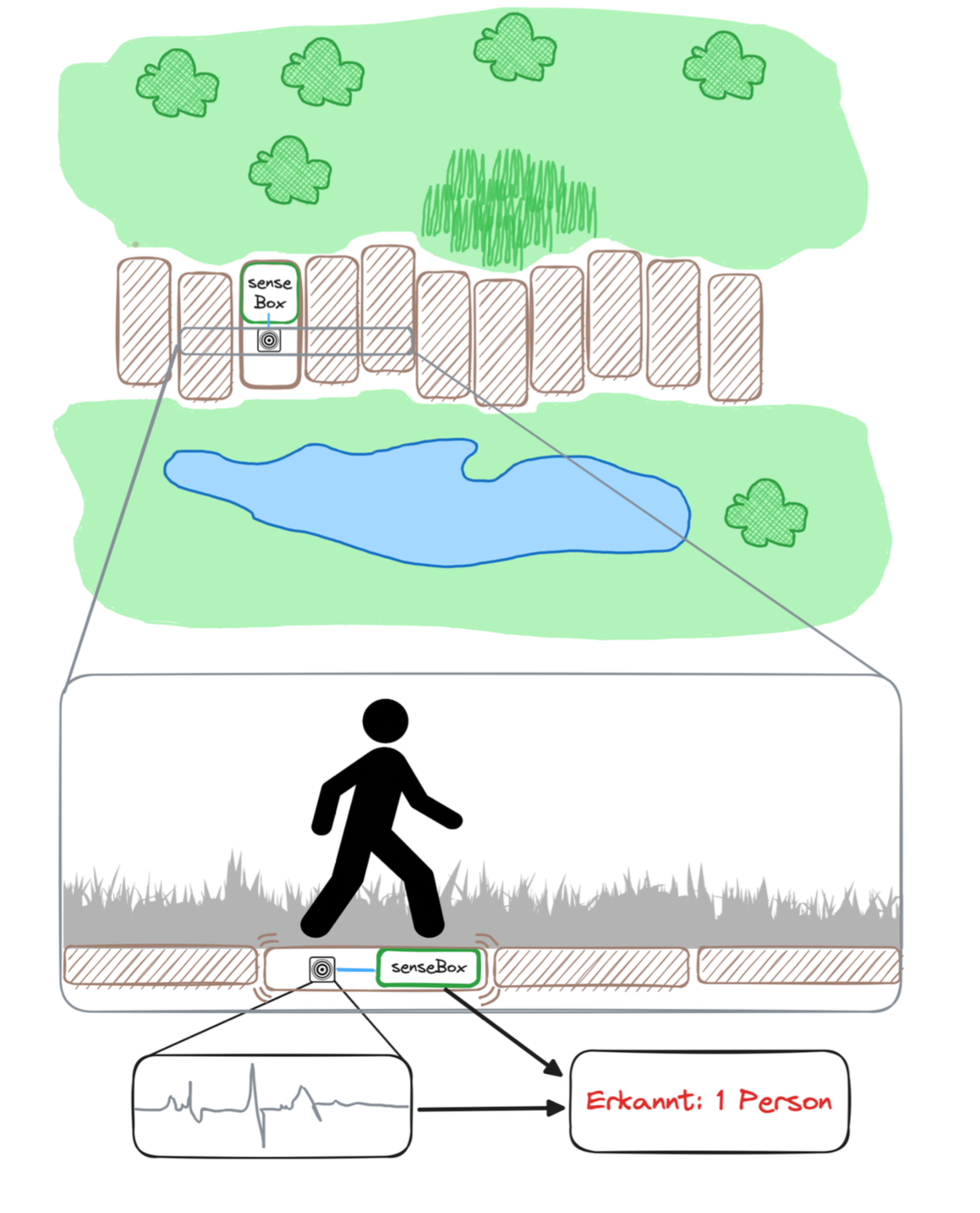
Counting people based on step vibrations
Relation to potential negative environmental impacts
Funding
