We want to make quantum sensors
Quantum sensor technology is a complex topic and raises big question marks on people's faces. What are quanta anyway? How can I use quantum sensing and what is it useful for? At QOOOL, we believe in the transformative power of quantum technology and are committed to promoting understanding of this fascinating technology. Our goal is to spark enthusiasm for quantum technologies, spread knowledge and develop innovative applications that fully exploit the potential of quantum sensing and make it usable in education. With sensor kits and interactive teaching and learning materials, the world of quanta can be experienced in the classroom, at university or by the general public.
Our partners

Reedu GmbH & Co. KG
Reedu GmbH & Co. KG from Münster is a start-up that emerged from the BMBF-funded senseBox project. Reedu manufactures the senseBox, a microcontroller for collecting environmental data. The company focuses on open sensor systems for end users and the education market. Open source components are used to create a wide range of products for citizens, students and pupils, enabling them to participate in citizen science. Reedu develops prototypes, driver and accompanying software for IoT products as well as effective educational solutions in the STEM field and organizes workshops and training courses for learners and teachers.

Institute for Micro Assembly Technology of the Hahn-Schickard-Gesellschaft
The Institute of Micro Assembly Technology at the Hahn-Schickard-Gesellschaft in Stuttgart has been working on the microintegration of complex, miniaturized systems for over 20 years. Its core competencies lie in technologies for spatial circuit carriers and microstructures as well as in connection technology, which is used for the integration of sensors in demanding environments. In the BMBF future cluster QSens, Hahn-Schickard is researching the encapsulation of quantum sensors and the thermal management of magnetic field sensors. In the QOOOL Sensing project, the institute is developing the quantum sensor module, the heart of the QOOOL kit.

Institute for Intelligent Sensors and Theoretical Electrical Engineering
The Institute for Intelligent Sensors and Theoretical Electrical Engineering (IIS) researches and implements new sensor concepts. In addition to the improvement of classical sensors, the focus is on miniaturized excitation and readout concepts for quantum sensors. With experience in miniaturization of nuclear and electron spin resonance, the IIS is working on CMOS-integrated microwave excitation concepts and ultra-low noise readout circuits for solid-state quantum sensors such as NV centers and silicon defects in SiC. In teaching, the IIS is responsible for electrodynamics and sensor and measurement technology and supervises the practical course “Build your own MRI”.

Department of Physics and its Didactics
Associated partners

LernortLabor - Bundesverband der Schülerlabore e.V.
LernortLabor - Bundesverband der Schülerlabore e.V. (LeLa) is the umbrella organization of school laboratories in German-speaking countries. As an interface to politics, business and science, LeLa promotes the expansion of the network as an integral part of the education system. The aim is to strengthen school laboratories and disseminate their special learning culture:independent, exploratory and research-based learning. The more than 500 registered school laboratories reach more than 1.3 million children and young people every year and cover topics ranging from career guidance to science communication.
Our vision:Quantum sensor technology for everyone
We encounter sensors everywhere in everyday life and they have found their way into our lives in many places. Modern sensors based on quantum technologies allow measurements with unimagined precision at the physical limit and thus provide access to previously unknown areas. Although quantum technology is highly functional, it is one thing above all:expensive! One reason for this is that diamonds are used as the main storage medium for quanta. The majority of the population has therefore had no direct contact with quantum technology such as quantum sensor technology; it remains an abstract and complex phenomenon. We want to change this:with low-cost hardware and didactic material as Open Educational Resources (OER), we want to sensitize and inspire broad sections of the population to quantum technologies through low-threshold access.
Development of the QOOOL kit
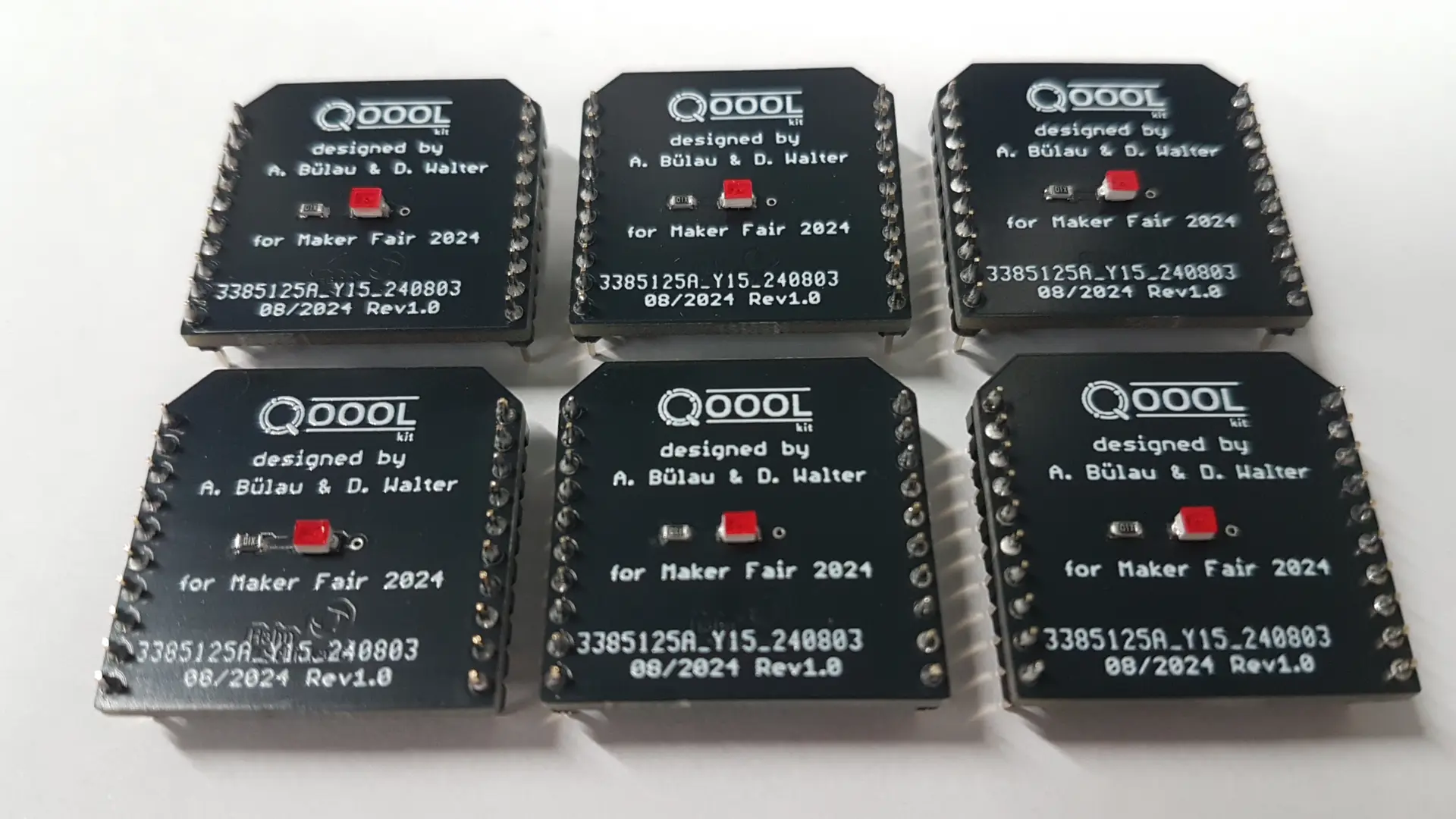

The chips that make quantum computing possible
As part of the QOOOL Sensing project, a robust magnetic field sensor is to be developed that enables low-threshold access to quantum sensor technology for different target groups. The sensor is based on specifically introduced defects in diamonds and allows highly accurate measurement of magnetic fields. The aim is to develop the first compact and cost-effective NV quantum magnetometer (NV = Nitrogen-Vacancy) in the form of a sensor kit (QOOOL Kit) for educational purposes, particularly in the STEM field. An integrated NV magnetometer in the form of a miniaturized sensor cell will then be used to carry out magnetic field measurements and make these observations available as open data on the web. The individual components of the kit will be designed in such a way that the sub-functions are comprehensible and their influence on the overall function of the sensor can be experienced in practice, e.g. through configuration options. The connection to the senseBox as a microcontroller for investigating environmental phenomena creates an all-round package with a wide range of possible applications.
Didactic concepts
In addition to the development of the QOOOL kit, practical and interactive teaching materials will be created to demonstrate the use of the sensor in the classroom, at university and for the general public. The (media-) didactically reduced processing of the QOOOL kit and the connection to the senseBox will be implemented through an interactive web application, online teacher training and other outreach activities such as makeathons, hackathons, workshops, etc. Project ideas, experiment instructions and didactic teaching material for STEM subjects will be made available as OER. The aim is to create widespread use in the areas of digital education and citizen science and to build a network with a creative community through the collaborative development of further educational materials.
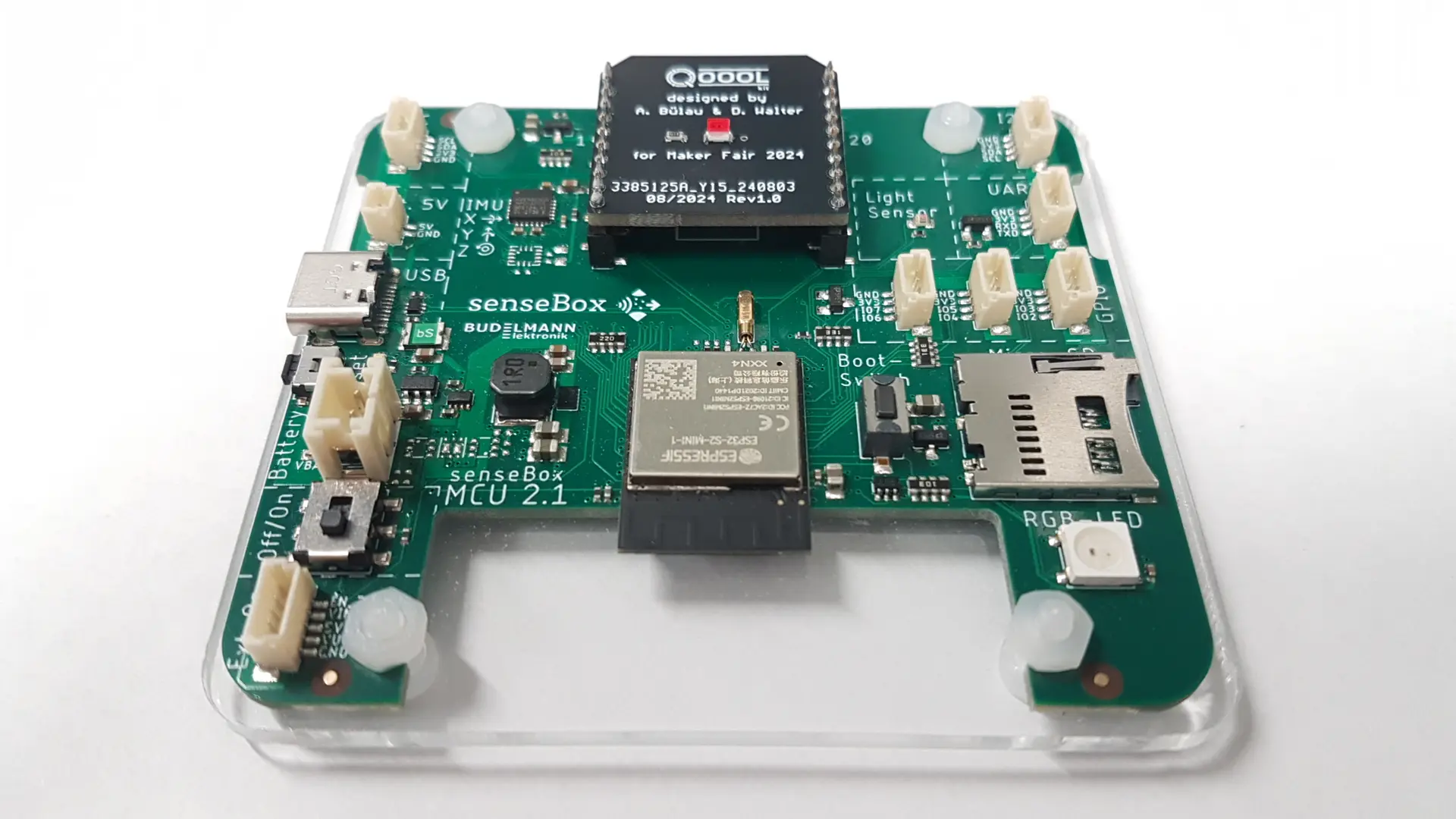

The senseBox-MCU S2 with the QOOOL-Kit
Simulator
The web-based application should be connected to the visual programming environment “Blockly for senseBox” and make program codes transferable not only to the senseBox hardware, but also to a simulator. In a visual simulation as a graphical representation of the QOOOL kit and the senseBox microcontroller, the functionality and implementation of the program code can be presented in a visually appealing and comprehensible way. The interactive learning software is intended to clearly explain the above-mentioned functionality and structure of an NV magnetometer as a quantum sensor and the interaction of its individual components.
Funding